with Automation Add-ins
Introduced in Excel 2002.
Automation add-ins must implement the System.Runtime.InteropServices.UnmanagedType.IDispatch interface.
Automation add-ins are loaded by the mscoree.dll.
The IDispatch interface is derived from the basic IUnknown COM interface.
Once the C# dll has been built it needs to be added to the registry using the RegAsm tool.
In addition to the normal COM Interop registration an additional registry entry is needed to register the functions.
This requires adding two additional class methods with the corresponding ComRegisterFunction attributes.
Excel will only recognise a COM Add-in as an Automation Add-in when the "Programmable" subkey is in the registry.
Creating
Open Visual Studio 2022 as Administrator.
New Project, Visual C#, Windows Desktop, Class Library (.NET Framework).
Change the Name to "ExcelAutomationAddin".
Change the Location to somewhere on your C drive.
Check the .NET Framework version is correct and press OK.
Rename the Class1.cs file to BetterFunctions.cs.
Add the following interface to the BetterFunctions.cs file:
namespace ExcelAutomationAddin
{
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.Guid("B2AEEA31-CB67-4F3E-9F6E-BA484B59D23C")]
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.InterfaceType(ComInterfaceType.InterfaceIsDual)]
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.ComVisible(true)]
public interface IBetterFunctions
{
string GetMyString();
string AddTwoNumbers(double value1, double value2);
}
}
Add the following class underneath the interface in the BetterFunctions.cs file:
namespace ExcelAutomationAddin
{
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.ProgId("ExcelAutomationAddin.BetterFunctions")]
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.ComDefaultInterface(typeof(IBetterFunctions))]
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.Guid("9819051F-E917-4841-8991-7FFBEC1187C9")]
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.ClassInterface(ClassInterfaceType.None)]
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.ComVisible(true)]
public class BetterFunctions : IBetterFunctions
{
public BetterFunctions()
{ }
public string GetMyString()
{
return "some text";
}
public string AddTwoNumbers(double value1, double value2)
{
return System.Convert.ToString(value1 + value2);
}
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.ComRegisterFunction]
public static void Method_RegisterFunctions(System.Type type)
{
// (64 bit Office)
Microsoft.Win32.Registry.ClassesRoot.CreateSubKey(
"CLSID\\{" + type.GUID.ToString().ToUpper() + "}\\" + "Programmable");
// (32 bit Office)
Microsoft.Win32.Registry.ClassesRoot.CreateSubKey(
"\\Wow6432Node\\CLSID\\{" + type.GUID.ToString().ToUpper() +
"}\\" + "Programmable");
}
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.ComUnregisterFunction]
public static void Method_UnregisterFunctions(System.Type type)
{
// (64 bit Office)
Microsoft.Win32.Registry.ClassesRoot.DeleteSubKey(
"CLSID\\{" + type.GUID.ToString().ToUpper() + "}\\" + "Programmable");
// (32 bit Office)
Microsoft.Win32.Registry.ClassesRoot.DeleteSubKey(
"\\Wow6432Node\\CLSID\\{" + type.GUID.ToString().ToUpper() +
"}\\" + "Programmable");
}
}
}
Make sure the 2 Guid Ids are replaced using (Tools > Create GUID).
Select (Build > Build Solution).
At this point no registry entries are automatically added in the registry.
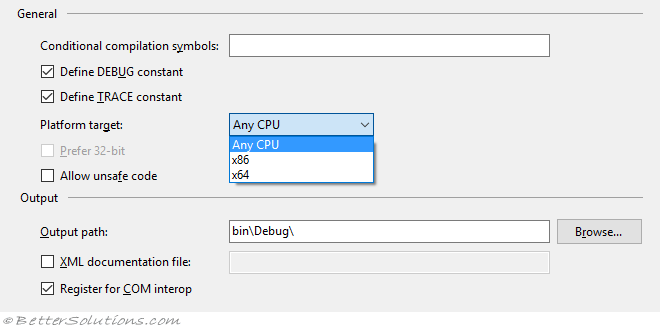
Select (Project > ExcelAutomationAddin Properties).
Display the Build tab.
Change the "Platform target" drop-down to "x86" for 32 bit machines.
Change the "Platform target" drop-down to "x64" for 64 bit machines.
Tick the "Register for COM Interop" checkbox (requires admin rights).
 |
Save and close the Properties window.
Select (Build > Build Solution).
When the solution is built a "TLB" file appears in the "\bin\Debug\" folder.
When the solution is built the RegAsm tool automatically runs.
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\ RegAsm /codebase ExcelAutomationAddin.dll
The RegAsm tool adds the necessary COM Interop class and interface information to the registry.
Using Early Binding
We can use Early Binding if we want to see what properties and methods are available in the VBA Object Browser.
Open Excel, Create a blank workbook.
Display the Visual Basic Editor (Alt + F11).
Add a new Code Module (Module1).
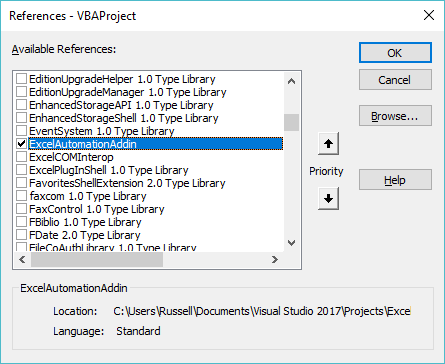
Select (Tools > References).
Find "ExcelAutomationAddin" in the list.
This dialog box displays a list of all the object libraries that are registered on that computer.
Tick this entry and select OK.
Early binding clients do not use the ProgID because the type library is referenced.
 |
Add the following code to Module1.
When you step through this code, you will see "some text" appear in the Immediate window.
Sub Call_EarlyBinding()
Dim objAddin As ExcelAutomationAddin.BetterFunctions
Set objAddin = New ExcelAutomationAddin.BetterFunctions
Debug.Print objAddin.GetMyString()
End Sub
Using Late Binding
We can also use Late Binding if we do not want a reference added to the project.
Late binding clients do use the ProgID.
Open Excel, Create a blank workbook, Add a new Code Module.
Add the following code to Module1.
When you step through the code, you will see "some text" appear in the Immediate window.
Sub Call_LateBinding
Dim objAddin As Variant
Set objAddin = CreateObject("ExcelAutomationAddin.BetterFunctions")
Debug.Print objAddin.GetMyString
End Sub
Registry Keys - Interface GUID
The registry keys that are generated are exactly the same as the COM Interop ones.
Registry Keys - Class GUID
The following ExcelAutomationAddin registry keys are added for the Class GUID:
HK_CLASSES_ROOT\ExcelAutomationAddin.BetterFunctions
HK_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Classes\ExcelAutomationAddin.BetterFunctions
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\ExcelAutomationAddin.BetterFunctions
(String)(Default) - ExcelAutomationAddin.BetterFunctions
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\ExcelAutomationAddin.BetterFunctions\CLSID
(String)(Default) - { class_GUID }
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Classes\ExcelAutomationAddin.BetterFunctions
(String)(Default) - ExcelAutomationAddin.BetterFunctions
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Classes\ExcelAutomationAddin.BetterFunctions\CLSID
(String)(Default) - { class_GUID }
The other registry keys that are generated are exactly the same as the COM Interop ones.
HK_CURRENT_USER\ExcelAutomationAddin.BetterFunctions\ CLSID
Registry Keys - Assembly GUID
The registry keys that are generated are exactly the same as the COM Interop ones.
ComRegisterFunction and ComUnregisterFunction
When a COM visible class is being registered for COM using the RegAsm utility you can perform additional actions when it is registered and unregistered.
These additional actions can be defined using the ComRegisterFunction attribute and the ComUnregisterFunction attribute.
These attributes have been added to the following class methods "Method_RegisterFunctions" and "Method_UnregisterFunctions".
In this example an additional "Programmable" registry entry is added when the project is built and the RegAsm tool runs.
The "Programmable" registry key is added in the following location:
// (64 bit Office)
HK_Classes_Root\CLSID\ { class_GUID } \ Programmable
// (32 bit Office)
HK_Classes_Root\Wow6432Node\CLSID\ { class_GUID } \ Programmable
MSCOREE.dll
Automation add-ins are loaded by the mscoree.dll.
// (64 bit Office)
HK_Classes_Root\CLSID\ { class_GUID } \ InprocServer32
(String)(Default) - C:\Windows\SysWow64\mscoree.dll
// (32 bit Office)
HK_Classes_Root\Wow6432Node\CLSID\ { class_GUID } \ InprocServer32
(String)(Default) - C:\Windows\System32\mscoree.dll
Sometimes Excel is not able to find this file when trying to load the Automation Add-in.
You can add an explicit folder location to get around this when the class is registered.
Append the following code to the end of the Method_RegisterFunctions method.
public static void Method_RegisterFunctions(System.Type type)
{
Microsoft.Win32.RegistryKey regkey;
// (64 bit Office)
regkey = Microsoft.Win32.Registry.ClassesRoot.OpenSubKey(
"CLSID\\{" + type.GUID.ToString().ToUpper() + "}\\" + "InprocServer32", true);
regkey.SetValue("", System.Environment.SystemDirectory + @"\mscoree.dll",
Microsoft.Win32.RegistryValueKind.String);
// (32 bit Office)
regkey = Microsoft.Win32.Registry.ClassesRoot.OpenSubKey(
"Wow6432Node\\CLSID\\{" + type.GUID.ToString().ToUpper() + "}\\" + "InprocServer32", true);
regkey.SetValue("", System.Environment.SystemDirectory + @"\mscoree.dll",
Microsoft.Win32.RegistryValueKind.String);
}
© 2024 Better Solutions Limited. All Rights Reserved. © 2024 Better Solutions Limited TopPrevNext