Tables
A continuous range or group of cells can be defined as a Table.
Tables were introduced in Excel 2003 but for some weird reason they were called Lists.
In 2007 the interface was changed to refer to these are tables.
However in the VBA object model though they are still identified as ListObjects.
Column headings always stay at the top when you scroll.
A list is just the name given to a table of data.
You can have multiple tables on the same worksheet.
When you create a list in Excel you should try and adhere to the following:
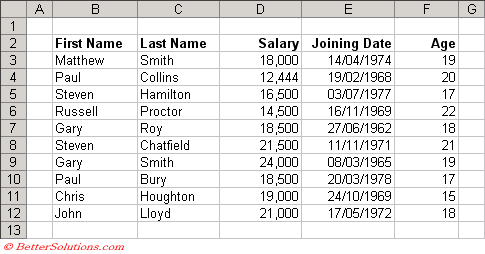
The first row should contain unique column labels.
Each column should contain a consistent type of data.
The information should be split into as many columns as possible to enable maximum sorting and filtering.
Try and avoid including any blank rows or columns. If you want to include spaces you should adjust the row height.
Each list should be placed on a separate worksheet.
 |
What is Filtering ?
This allows you to hide rows that do not match your criteria.
Filtering a list or table of data can be useful especially when you want to find a particular record.
There are two types of filtering that can be used AutoFilter and Advanced Filter.
AutoFilter is for simple criteria and Advanced Filter is for more complex criteria.
You can apply filtering to a list or table by selecting (Data > Filter) sub menu.
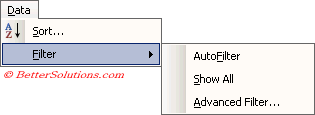 |
The Show All command can be used to reset your filter to display all the rows.
AutoComplete
AutoComplete is the automatic filling in of your text when you start typing and is switched on by default
AutoComplete matches only exact cell entries, not individual words in a cell. This does not work when entering or editing formulas.
The AutoComplete and Pick From List features make it a lot quicker to enter repetitive text.
AutoFilter
When you create tables, filters are added automatically in 2010 and 2007 ?
You can easily toggle these filters (Data tab, filters)
Advanced Filter
This is for more complex filtering
The main difference with this is that the criteria is specified in a range of cells separate from your data list.
The field names that appear in the header rows can be used to identify the columns you want to apply filters to.
To apply an Advanced Filter just select any cell in the list of data and select (Data > Filter > Advanced).
There must be at least one blank row or column separating the criteria and the data list.
Click in the Total row displays a drop-down of quick functions to insert
Options
(Edit tab, Extend data range formats and formulas) - Formulas that contain references to ranges will be automatically expanded when new cells are inserted to the right or below the existing range. This only works when cells are inserted immediately below or to the right of a referenced range.
(Formulas tab, Error Checking rules)(Formulas inconsistent with other formulas in the region)
The status bar displays "Filter Mode"
When you filter a list (or table) on a worksheet the status bar changes to display the number of records found.
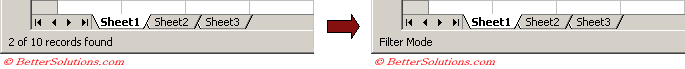 |
This message is not displayed if the status bar is changed before the filter is completed.
This message will be changed to "Filter Mode" if any of the following actions are performed:
1) A cell is formatted.
2) The contents of any cells are deleted.
3) Another worksheet is activated.
_filterdatabase - Worksheet Level Named Range
After you have applied the AutoFilter or used an Advanced Filter the corresponding table will be given the named range "_filterdatabase".
This named range is assigned automatically and will not appear in the Name Box or in any of the the (Insert > Name) dialog boxes.
This worksheet level named range is automatically reassigned to the corresponding table whenever you use the AutoFilter or Advanced Filter.
The "_filterdatabse" is not case sensitive but can be used to quickly select the whole table.
Select (Edit > GoTo) and type in "_filterdatabase" and press OK.
You could always define this named range manually to ensure that the correct cell reference is always entered into the "List range" field of the Advanced Filter.
If the named range is defined manually any cell can be selected before you select (Data > Filter > Advanced Filter).
Large range of cells
add an autofilter
filter on one particular column - all numbers in a particular range 0 < - < 10
select visible in a column block and shade
repeat for another range of numbers ??
Important
When you apply a filter the original data is unchanged, the rows that do not match are just hidden temporarily.
Excel only allows one list to be filtered on a worksheet at any one time.
© 2026 Better Solutions Limited. All Rights Reserved. © 2026 Better Solutions Limited TopNext