Questions - Physics
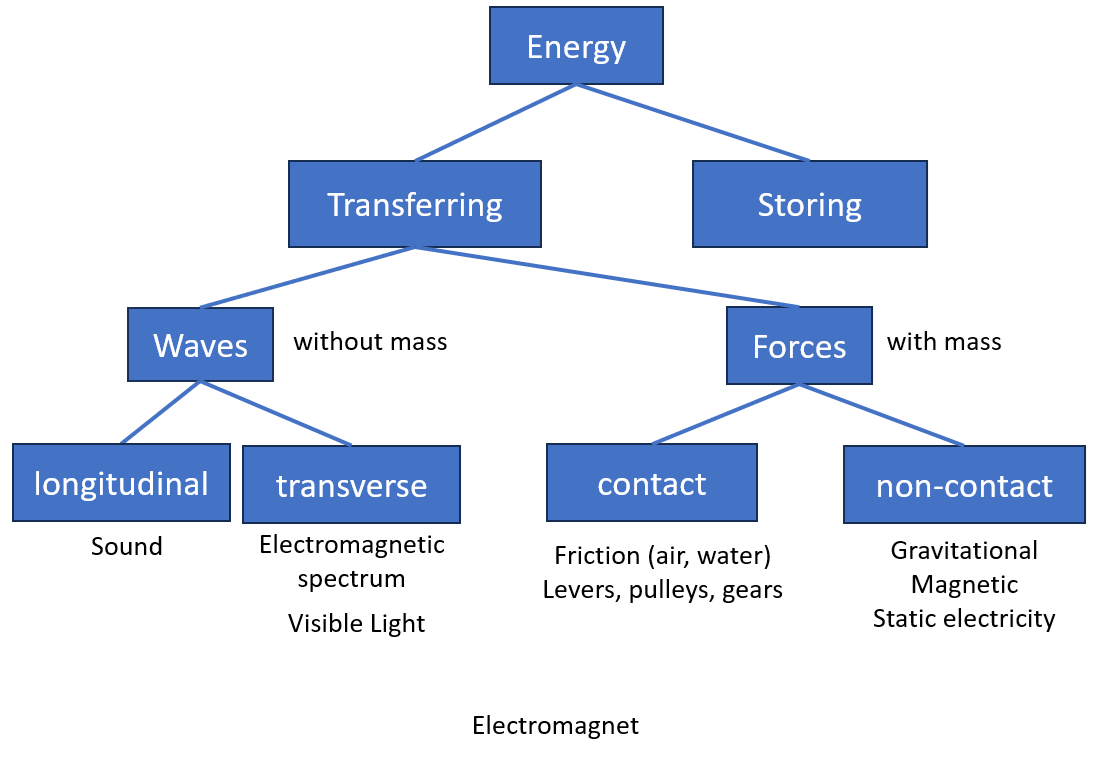 |
Energy
1) What is Energy ?
Energy is the ability to do work.
Energy (J) = Power (w) x Time (s)
2) What are the eight different ways that energy can be stored ?
Kinetic - (movement) anything that moves has energy.
Elastic - anything stretched (eg springs, rubber bands)
Chemical - anything that can release energy by a chemical reaction (eg batteries, food, fuel)
Thermal - anything that is hot
Gravitational - anything in a gravitational field, the higher the object the more energy
Magnetic - two magnets attract or repel (north/south)
Electrostatic - two electric charges attract or repel (positive/negative), static electricity
Nuclear - involves splitting or fusing atoms
3) Can energy be used up ?
Energy is not destroyed, it is just transferred and conserved.
Energy is only useful when it is transferred.
When energy is transferred some of it will be wasted, typically by some form of heating.
4) What is Potential Energy ?
This is the energy that is stored in an object because of its position, stresses within itself, its electric charge or other factors.
Examples include: gravitational, elastic, magnetic, chemical, electrostatic, nuclear
5) Can you describe Energy Transfer ?
Energy can be transferred by doing work.
Energy can be transferred from one object to another.
Energy can be transferred between the different energy stores of the same object (eg kinetic to thermal)
6) What is a Closed System ?
This is an object where energy (or matter) cannot leave or enter.
The total amount of energy in a closed system remains constant.
7) Can you give some examples of energy transfer ?
Dropping an object - the object moves through the gravitational field.
energy moves from Gravitational to Kinetic
energy is transferred Mechnically (using the gravitational force)
Throwing a ball -
energy moves from Chemical to Kinetic
energy is transferred Mechnically (using a force)
Burning wood -
energy moves from Chemical to Thermal
energy is transferred by Heating
Stretching a Spring -
energy moves from Elastic to Kinetic
energy is transferred Mechnically
8) If you move an object (mechanically using a force) where is the energy transferred to ?
The energy required to move the object is transferred to the objects Kinetic energy store.
9) What is the formula for Kinetic Energy ?
Anything that is moving has kinetic energy, measured in Joules.
How much energy depends on the mass and the speed of the object.
E(k) = 1/2mv2
m = mass (kg), v = speed (m/s)
10) What is the formula for Gravitational Energy ?
How much energy depends on the mass, height and strength of the gravitational field.
E(g) = mgh
m = mass (kg), g = field strength (N/Kg), h = height (m)
11) What is the formula for Elastic Energy ?
E(e) = 1/2ke2
k = spring constant (N/m), e = extension (m)
12) What are the different ways that energy can be transferred ?
Radiation - (using waves) a vibration where matter does not move.
Mechanically - (using forces) when a force makes matter move (push, pull, stretch, squash)
Electrically - when electric charges moves around an electric circuit because of potential difference
Heating - (conduction, convection) when two objects are at different temperatures. Energy is transferred from the hotter to the cooler
13) If energy is transferred using Heating what is Thermal Equilibrium ?
Thermal energy will continue to be transferred until both objects reach the same temperature.
When the objects are the same temperature they have reached thermal equilibrium.
14) Can you describe Radiation ?
All objects send out invisible waves called radiation to their surroundings.
Two objects do not have to be touching for energy to be transferred using radiation.
15) We can be divide radiation into two categories, what are the two categories ?
Non-Ionising Radiation - (low frequency) A low-energy radiation that can pass through the body without being absorbed.
Ionising Radiation - (high frequency) They remove electrons from atoms to create positive ions. These waves can interact directly with a DNA molecule's atoms and prevent them from reproducing. Ultraviolet waves (found naturally in sunlight), X-rays and gamma rays
16) What are the different types of Radiation ?
All radiation can travel through solid objects, air and even vacuums.
Electromagnetic - These have no mass or charge. Synchronized oscillation of electric and magnetic fields. All transverse waves. All travel at very high speeds.
Alpha - when an alpha particle (2 protons & 2 neutrons) is emitted from the nucleus
Beta - when an electron is released by the nucleus
Neutrons - when a particle that has no charge is present in the nucleus of an atom
17) What is the Electromagnetic Spectrum ?
This is a list of the seven different groups of waves that make up Electromagnetic Radiation, with lowest frequency first (highest wavelength first)
Roman Men Invented Very Unusual Xray Glasses
Radio waves
These are waves with the lowest frequency in the electromagnetic spectrum
Microwaves
These are waves of the electromagnetic spectrum that can be used for heating or communicating
Infared waves
These are used for remote controls and heaters
Visible light
These are used for optical fibres and photography
Ultraviolet light
These can harm the human body, causes skin to age prematurely and increase the risk of skin cancer, used by sunbeds.
X-rays
These can harm the human body, These waves are not transmitted through bones.
Gamma rays
These can harm the human body, cause ionisation inside cells. This damage leads to the cells dying.
18) Do all Electromagnet Waves have the same wavelength ?
No.
19) What does the Radiation Dose tell you ?
This is a measure of the risk of harm to human body tissue when exposed to radiation.
It is measured in Sieverts (Sv)
20) Which group of electromagnetic waves has the shortest wavelength ?
Gamma rays have the shortest wavelength
Radio waves have the longest wavelength
21) Can you describe Conduction ?
Occurs mainly in solids
When an object is heated the particles have more energy and this energy is transferred when two objects are touching.
The particles vibrate more and collide with each other. These collisions cause energy to be transferred between the particles.
Energy is transferred to the Thermal energy store.
Thermal conductivity is a measure of how quickly energy is transferred with conduction.
22) Can you describe Convection ?
Occurs mainly in liquids and gases
Convection occurs when particles with a lot of heat energy in a liquid or gas move and take the place of particles with less heat energy.
The particles can already move around in liquids and gases, but they move faster and space between the individual particles increases.
The density of the heated area will decrease.
radiators work by using convection in a gas.They heat the air near the radiator, reducing its density and making it rise.
lava lamps work by using convection in a liquid
23) What does the Specific Heat Capacity" of an object tell us about Thermal Energy ?
It indicates how easy (or hard) it is to heat up an object.
This is the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1Kg of a substance by 1 degree celcius.
24) What is the formula for Thermal Heat Capacity ?
change in thermal energy = mass × specific heat capacity × temperature change
25) What is a Mechnical Wave ?
This is a wave that is an oscillation of matter and requires vibration in a solid, liquid or gas.
These can travel through air and solid materials (not through a vacuum)
26) What is Movement ?
The change in position of an object.
27) What is Motion ?
The action or process of "moving" or "changing" place or position.
28) How can the efficiency of energy transfer be calculated ?
Efficiency = Useful Output Energy / Total Input energy
The efficiency of energy transfer can be improved by insulating objects, lubricating or by streamlining.
29) The energy resources available on Earth can be divided into two categories, what are the two categories ?
Non-Renewable - Coal, Oil, Gas
Renewable - Sun, Wind, Water Waves, Water Tides, Hydro-electric, Biofuel, Geothermal
Electricity
30) What is an Atom ?
This is the smallest unit of matter.
An atom can contain positive and negative charge
It is composed of three sub-atomic particles:
Proton - (found inside the nucleus) This is the positive charge (these cannot move)
Electron - (found outside the nucleus) This has the negative charge (these can move)
Neutron - (found inside the nucleus) This has a neutral charge
31) How does an object become positively charged ?
The object has to lose electrons (leaving more positive charge)
32) How does an object become negatively charged ?
The object has to gain electrons (increasing its negative charge)
33) What is an Electric Field ?
This refers to the area around an object that is affected by an electric force (non contact)
The electric field can be illustrated with a diagram showing arrows.
The direction of the arrow shows the direction a positive charge will be pushed.
It points towards the negative charge.
The closer together the arrows are, the stronger the field.
34) Can electric forces affect the air around them ?
Yes. An object that has an electric force can affect another object without the objects touching.
35) What happens when these two charged objects get close together ?
Positive + Positive - They repel each other.
Positive + Negative - They attract each other.
36) What is Static Electricity ?
When electric charge is not flowing it is called static electricity
When two insulating objects are rubbed together electrons are transferred from one object to the other.
37) What is Electricity ?
This is the name given to the type of energy created when electric current flows through a circuit.
Electricity is the flow (or movement) of electrons in a circuit.
Electric current flows from a power supply in a loop around a circuit and back to the power supply.
Anything that needs electricity to work is called an electrical appliance.
38) What is an Electric Current ?
Electric current is the flow of negative charge (or electrons) around a circuit.
The amount of electrons that are moving is called the current.
Current can only flow if a circuit is complete with no gaps.
39) Does an Electric Current generate an electric field ?
Yes.
40) Does an Electric Current generate a magnetic field ?
Yes. You can see this by putting a compass near an electric current.
41) Does current get used up ?
Current is not used up.
The total current is always the same.
42) What is a Battery ?
It contains energy that can be used to transfer chemical energy into an electric current.
A battery provides the force that can push electric charge around a circuit.
A battery will have a potential difference rating
43) What is Potential Difference ?
Another word for potential difference is Voltage.
The Potential Difference is the force that pushes the electrons (negative charge) around the circuit.
If you increase the potential difference more current will flow.
44) What is a Transformer ?
A transformer is a device that can change the potential difference or voltage of an alternating current.
A basic transformer is made from two coils of wire, a primary coil from the alternating current (ac) input and a secondary coil leading to the ac output.
The coils are not electrically connected. Instead, they are wound around an iron core.
This is easily magnetised and can carry 'magnetic fields ' from the primary coil to the secondary coil.
45) What are the two different types of transformers called ?
Step Up and Step Down
46) What is Resistance ?
Resistance is what slows down the electrons / flow of current.
Resistance is measured in Ohms
Resistence = Potential Difference / Current
The lower the resistance the better the material is at conducting electricity.
Wood has a very high resistance. Metal has a very low resistance.
47) What are Conductors ?
Conductors are materials that allow electricity to pass through them easily (eg metals)
The lower the resistence the better it is at conducting electricity.
48) What are Insulators ?
Insulators are materials that do not allow electricity to pass through them easily (eg wood)
49) What is an Ammeter ?
This is a device used to measure the Current in a circuit.
Current (A) = Potential Difference (v) / Resistance (R)
It is measured in Amperes (A)
50) What is a Voltmeter ?
This is a device used to measure the Potential Difference (or Voltage) in a circuit.
To measure the potential difference you need to measure it between two different points on the circuit.
It is measured in Volts (V)
51) What is a Bulb ?
A bulb will tell you the maximum potential difference that you can safely put through it.
52) What is a Circuit Diagram ?
A drawing that uses circuit symbols to show all the components in a circuit and how they are connected.
Cell - single energy source
Battery - multiple energy sources
Switch - these can be switches on or off, when off, the switch is open
Bulb - device that produces light from an electric current
Buzzer -
Voltmeter - an instrument measuring the volts
Ammeter - an instrument measuring the amps
53) What is a Series Circuit ?
There is only one route that the current can take
54) What is a Parallel Circuit ?
There is more than one route that the current can take
55) Can you describe some facts about parallel circuits ?
when the current is split into different branches the current is divided.
the current after a join is the total of all the branches
the current may not be the same everywhere
Magnetism
56) What is a Magnet ?
Some elements have an atomic structure that creates a magnetic field.
They are objects that produce magnetic fields (metals - iron, nickel, cobalt)
They can be made permanently magnetic by exposing them to a magnetic field using eletric current.
57) How do you make a permanent magnet ?
A magnetic field is created when electrons move around the neucleus.
Some elements have an atomic structure that allow the negatively charged particles (electrons) to move around the nucleus (that contains the proton and neutron)
When the electrons are in motion, they create a magnetic field.
Elements that have strong magnetic behaviour are called ferromagnetic elements.
58) What is Steel made up of ?
Steel is an alloy that is a substance formed by combining two or more metals.
Steel is a combination of Iron, Carbon (<2%) and other elements.
Steel is mostly iron, so is magnetic.
59) What is a Solenoid ?
This is a long coil of wire.
60) What is a Magnetic Field ?
This refers to the area around an object that is affected by a magnetic force (non contact)
61) Can magnetic forces affect the air around them ?
Yes. An object that has a magnetic force can affect another object without the objects touching.
62) Can you give the names of some metals that have a very low magnetic field ?
Most metals have a very low magnetic field, gold, silver, aluminium.
63) What is Brass mad up of ?
Brass is a combination of Copper and Zinc.
64) Can you draw the magnetic field lines for a bar magnet ?
North pole and South pole
65) What happens when these two poles get closer together ?
North + North - They Repel each other.
North + South - They Attract each other.
66) What is an Electromagnet ?
This is a magnet that can be switched on and off.
An electric current flowing through a coil of wire, will create a magnetic field.
Because you can turn the current on and off, you can therefore turn the magnetic field on and off.
Iron is used to create electromagnets.
67) What is an Electromagnetic Field ?
When an electric field and a magnetic field join together this combined field is called an electromagnetic field (EMF).
This invisible field is often called radiation.
68) Can you describe the magnetic field produced when current flows through a wire ?
When a current flows in a wire, it creates a circular magnetic field around the wire.
The direction of the current and magnetic field can be found using the right hand grip rule.
69) How could you increase the magnetic strength of an electromagnet ?
There are two ways:
Increase the current
Increase the number of turns in the coil
70) Can you describe how you build an electric motor ?
It is made from a loop of wire between two magnets
When current flows through the wire, a magnetic field is created around the wire
The magnetic field from the wire is attracted and repelled from the magnets that are stationary.
This force causes the top of wire to turn.
Waves
71) What is a Wave ?
A wave is a vibration that transports energy from one place to another without transporting mass.
All objects send out invisible waves called radiation to their surroundings.
The matter does not move.
72) What are the three different ways of categorising waves in terms of the direction of particle movement ?
Longitudinal - (sound)
Transverse - (electromagnetic, inc light) and stretched springs
Surface -
73) What is a Longitudinal Wave ?
When the direction of the vibration is in the same as that of the wave
The particles oscillate parallel to the direction of the energy.
The particles vibrate (or oscillate) and pass the energy onto the next particle.
Needs a medium to travel through.
74) What is a Transverse Wave ?
When the direction of the vibration is perpendicular to that of the wave.
The particles oscillate perpendicular to the direction of the energy.
Does not need a medium to travel through.
75) What is the Frequency of a wave ?
The number of waves produced in one second, measured in hertz.
76) What is the Period of a wave ?
The time it takes for a full wave to pass a given point, measure in seconds.
This is 1 divided by frequency.
77) What is the Wavelength of a wave ?
The distance between two corresponding points on a wave, in metres.
78) What is the Amplitude of a wave ?
The distance from the middle to either the top or bottom.
The maximum amount of vibration, usually measured in metres
79) What is the difference between the Crest and the Trough ?
Crest (or Peak) - the top of a wave.
Trough - the bottom of a wave.
80) What is the relationship between Frequency and Wavelength ?
The higher the frequency, the shorter the wavelength
The lower the frequency, the longer the wavelength
Frequency and wavelength are inversely proportional to each other.
81) How do you calculate Wave Speed ?
Speed = Frequency x Wavelength
82) What are the units for Wave Speed ?
Metres per Second
83) Does the speed of a wave have anything to do with the Amplitude ?
No. The size of the wave does not affect the speed.
84) What is Transmission ?
This is where the waves travel through a medium rather than being absorbed or reflected
85) What is Absorption ?
When energy is transferred from sound (or other types of waves) to a material
86) What is Displacement ?
Calculate the speed of a wave that has a wavelength of 42 cm and a frequency of 11 hertz.
speed = frequency x wavelength
87) What is a Mechanical Wave ?
This is a wave that is an oscillation of matter and requires vibration in a solid, liquid or gas.
They can travel through air and solid materials.
Examples include - sound, water, stretched string
88) What is Sound ?
These are longitudinal waves that need a medium to travel through.
It is impossible for sound to travel through a vacuum because there are no air molecules to vibrate.
89) What is the speed of Sound ?
The distance sound travel in one second (330 m/s)
90) What is a Pressure Wave ?
It is a wave that has a repeating pattern of high pressure regions and low pressure regions (for example sound)
91) What is an Oscilloscope ?
A device that is able to view patterns of sound waves that have been turned into electrical signals.
92) How does Frequency affect Sound ?
93) What is the Pitch of a wave ?
94) How are Pitch and Frequency related ?
A low pitch sound has a low frequency.
A high pitch sound has a high frequency.
95) How does a Loudspeaker work ?
It uses an electromagnet to make sound from a varying potential difference.
It turns an electrical signal into a pressure wave of sound.
The changing P.d. causes changes in air pressure.
96) How does a Microphone work ?
sound can be detected with a microphone.
It turns any pressure waves that hit is into an electrical signal (or potential difference)
97) What do you need to do to a sound wave to make it louder ?
Increase the amplitude.
98) What is an Echo ?
Reflection of sound waves from a surface back to the listener
99) Can you give the names of some of the bones in the inner ear ?
hammer, anvil, stirrup
100) Can you give the names of some of the bones in the outer ear ?
pinna, auditory canal, eardrum
101) What is Ultrasound ?
Sound at a frequency greater than 20,000 Hz
this is beyond the range of human hearing
102) What frequency can humans hear ?
Between 20-20,000 Hz
103) What are Decibels ?
The unit used to measure the loudness of sound.
104) What is Visible Light ?
These are transverse waves that do not need a medium to travel through.
They have a frequency that human eyes can detect.
105) What is the speed of Light ?
The distance light travels in one second (300 million m/s)
106) What is Ultraviolet light ?
These are light waves that have a higher frequency than the light that human eyes can detect.
107) What are the 3 Primary colours ?
Red, Blue, Green
All colours can be broken down into different combinations of the three primary colors.
108) What is a Secondary colour ?
It is a colour obtained by mixing two primary colours together.
R + B = Magenta
R + G = Yellow
B + G = Cyan
109) What colour would these objects be ?
blue object in blue light (blue)
blue object in red light (black)
blue object in green light (black)
yellow object in red light (red)
yellow object in blue light (black)
110) What is Angle of Incidence ?
The angle between the normal and incident ray
111) What is Angle of Reflection ?
The angle between the normal and the reflected ray
112) What is the Law of Reflection ?
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
113) What is a Lens ?
A device made up shaped glass that focusses light rays from objects to form an image
114) What is the difference between a Concave Lens and a Convex Lens ?
Concave - A lens that is thinner in the middle and that spreads out light rays
Convex - A lens that is thicker in the middle and that bends light rays towards each other
115) What is a Shadow ?
A shadow is formed when light travelling in straight lines from a light source is blocked by an opaque object.
116) What is a Mirror ?
Is an object that reflects light at the same angle that it hits.
117) What is Converging ?
Bringing rays of light together
118) What is Dispersion ?
Splitting up of a ray of light of mixed wavelengths into separate components by using refraction
119) What is Diverging ?
The type of lens that spreads light out and forms a virtual image
120) What is the Focal Point ?
The point at which light rays refracted by a convex lens cross over
121) What is an Incident Ray ?
The incoming ray from a source of light
122) What is an Reflected Ray ?
Light rays that are bounced off a surface.
123) What is Opaque ?
A material that does not allow light to pass through it
124) What is a Non-Luminous object ?
An object that produces no light.
125) What is the optic nerve ?
A pair of sensory nerves that run from each eye to the brain.
126) What are the difference parts of the eye called ?
Pupil - the hole in front of your eye called where light goes in.
Iris - the coloured part of your eye called.
Retina - the back of the eye where the image is formed.
Cornea - the transparent layer at the front that refracts light.
127) What is Refraction ?
This is when light bends when it crosses a boundary between two different substances.
128) What is a Spectrum ?
A band of light produced when light is spread out by a prism.
129) What is a Translucent material ?
A material that allows some light to pass through it
130) What is a Transparent material ?
A material that allows all light to pass through it.
Forces
131) What is a Force ?
They are usually pushes or pulls. (they can also be twists)
A force always acts in a certain direction.
Forces normally occur between two objects that are touching (or in contact)
However some forces can occur without contact.
132) Forces can be used to make objects do 7 things, what are they ?
make an object start moving / constant speed
make an object stop moving
speed up / accelerate
slow down / decelerate
change direction
turn/pivot/twist
change shape/deform
133) Can you give some example of Contact Forces ?
Friction, Upthrust
134) Can you give some examples of Non-Contact Forces ?
Gravity - (gravitational force) everything falls to the floor
Magnet - (magnetic force) magnets will attract paper clips towards it
Static Electricity - (electric force) electric charge that is not flowing (static charge on a balloon)
A field is a region where an object experiences a non-contact force.
135) What is aerodynamic lift ?
136) How are forces measured, what is the unit ?
Newtons (N)
137) What is the difference between balanced and unbalanced forces ?
Balanced forces - are equal in size but opposite in direction. The net force is zero. Objects can be stationary or moving at a constant velocity. Also called a Reaction force.
Unbalanced forces - are not equal in size or not in the same direction.
138) What is Friction ?
Friction is a contact force that always acts in the opposite direction to the movement.
For an object to move the force must be larger than the friction (or resisting force).
Friction only occurs when an object is moving and two surfaces rub together.
When an object tries to pass through a gas or liquid there will be some friction/resistance.
The rougher the surface, the more friction there is.
139) What is Air Resistance ?
This is a frictional force that pushes against the object trying to move through the air, also referred to as drag.
The faster the object moves the greater the resistance.
When the frictional force equals the opposing force the object moves at a steady speed.
The fastest car on land travelled at 763 mph.
140) What is Water Resistance ?
This is a frictional force that slows objects down when they pass through water, also referred to as drag.
The fastest boat on water travelled 316 mph.
The fastest submarine travelled at 51 mph (44 knots).
141) What is Weight ?
The force acting on an object because of gravity.
Often referred to as Mass.
142) What is Density ?
This is how heavy a material is for its size.
This is a measure of how many particles there are in a given space.
Density is the amount of mass in a given volume. How closely packed they are.
143) What is the formula that connects density, mass and volume ?
density = mass / volume
144) Can you describe the density in solids, liquids and gases ?
Solids usually have a higher density than liquids.
Liquids usually have a higher density than gases.
When a solid is heated, the particles move around more and move further apart
The substance expands and becomes less dense.
Solid to Liquid, density decreases, volume increases
Liquid to Solid, density increases, volume decreases.
145) When H2O changes from a liquid to a solid, does the density increase ?
No. H2O is the only known non-metallic substance that actually expands when it changes from liquid to solid.
Its density actually decreases and it expands approximately by 9% volume.
146) When ice melts, does its volume increase or decrease ?
This is solid to liquid, density decreases, volume increases.
147) Why do icebergs float ?
The density of ice is lower than the density of water.
148) What is the opposite of Expand ?
Contract.
149) What is a Force Diagram ?
It is a drawing with arrows to show all the forces acting on an object.
150) What is Upthrust ?
This is a contact force that pushes things upwards.
In liquids the pressure increases with depth due to the weight of the water above it.
Liquid pressure causes upthrust and makes things float.
151) When does an object sink ?
If the object is denser than the liquid, the object will sink.
Salty water is denser than pure water, which makes it easier for objects to float.
152) How can a large ship float ?
There is a lot of air inside the ship which means that it is not as dense as water.
If the upthrust is equal to the objects weight, the object will float.
The force pushing upwards at the bottom of the object is greater than the force pushing down at the top of the object.
153) Why do helium balloons float in air ?
Anything that is less dense than air will float, although air is not very dense.
154) When is there a change in speed or direction ?
There is a change in speed or direction when the forces are unbalanced
155) When forces make an object turn, what is the Moment ?
The moment is the name given to the force that is creating the turning effect
When a force acts on something that has a pivot, it creates a moment (or turning effect)
Moment = Force x Distance
156) What are Levers, Pulleys and Gears ?
A lever uses force on a pivot to lift the load.
A pulley uses a flexible cable across a wheel to lift the load.
A gear uses wheels with teeth to transfer motion and power from one to another.
157) What is Tension ?
State of being stretched tightly.
158) How can you Deform an object ?
You can use forces to stretch or compress objects
When an object deforms it changes its shape
A spring is an example of an object that can compress
159) What is Hooke's law ?
This only applies to Springs.
This says the amount it stretches (the extension) is directly proportional to the force applied (the weight).
For springs, the force at which Hooke's law stops working is much higher than for most materials, springs are unusual.
F = ke
160) What is Compression ?
A force that is squashing or pushing that changes the shape of an object
161) How does an Insulator effect the rate of energy transfer ?
Some materials transfer energy faster than others.
Materials that transfer energy slowly (using conduction) are called insulators.
Insulators help to keep hot objects hot and cold objects cold.
162) What are the different Energy Resources ?
Most of our energy originates from the sun.
Fossil Fuels (non-renewable) - Sun - Light - Photosynthesis - Dead Plants/Animals - Fossil Fuels
Biomass - Sun - Light - Plants - Photosynthesis - Biomass
Wind - Sun - Light - Heats atmosphere - Air Moves - Wind
Wave - Sun - Light - Heats atmosphere - Air Moves - Wind - Waves
Solar - Sun - Light - Solar Cells - Electricity
163) Describe how electricity can be generated from fossil fuels ?
Fuel is burnt and water is turned into steam. Energy is transferred from Chemical to Thermal.
The thermal energy is then transferred to Kinetic energy used to drive a Turbine which generates the electricity.
The kinetic energy is then transferred into electricity.
164) What does the power rating of an electrical appliance tell you ?
This tells you how fast the energy will be transferred.
165) What is Power and how is it measured ?
Electric power is the rate of transfer of electrical energy within a circuit.
Power is usually measured in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW).
166) What units are used for Energy transfer ?
Joules (J)
Kilojoules (kJ) - all food is measured in kJ
Kilowatt-hours (kWh)
167) Calculate the energy transferred by a 1.5 kW remote control car used for 1 hour.
Energy Transferred = Power (W) x Time (seconds)
Energy = 1500 x 3600 ??
Energy Transferred = Power (kW) x Time (hours)
Energy = 1.5 kWh
168) What will transfer more energy, a 200W device left on for an hour or a 300W device left on for an hour.
The 300W because it has a higher power rating.
169) Two identical cranes can transfer 20 KJ of energy to lift an object. Which crane can lift the object the highest ?
One crane applies a big force and the other crane applies a small force.
A large force can be applied over a small distance.
A small force can be applied over a large distance.
170) What is Speed ?
Speed is a measure of how far you travel in a given amount of time.
Speed is Distance over Time.
171) What is Velocity ?
Velocity is speed in a particular direction.
172) What are the 3 common units of speed ?
metres per second (m/s), miles per hour (mph), kilometres per hour (km/h).
173) What does the gradient show on a Distance-Time Graph ?
The gradient on a distance-time graph is the speed of the object.
The steeper the line, the faster the object is moving.
174) What does a straight line show on a distance-time graph ?
A straight line represents a constant speed.
175) Can you describe Brownian Motion ?
This is the random motion of particles in a fluid resulting from their collision with the fast moving atoms in the fluid.
Solar
176) What are the names of the Planets in our Solar System ?
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
177) Is the Sun a planet or a star ?
A star, which gives out light. It's the closes star to Earth.
178) What is a Galaxy ?
It's a large group of stars.
179) What is the definition of the Universe ?
It is made up of billions of gallaxies.
180) What is the name of the galaxy that contains the Sun and Earth ?
The Milky Way which contains billions of stars.
181) What is Gravity ?
This is an invisible force that pulls you to the ground.
All objects have gravity and make a slight pull on other objects.
Huge objects like planets and stars have enough gravity to pull other things towards them.
182) What is Gravitational Force ?
This is the force caused by gravity.
183) Is there gravitational forces in a vaccuum ?
Yes. It does not depend on air.
184) Which planet has a larger gravitational force, Earth or Jupiter ?
The larger the planet the greater the gravitational force.
The gravity on Jupiter is twice as strong as the gravity on Earth.
185) How strong is the gravitational force from the Moon ?
High and low tides are caused by the gravitational force of the moon (and to a lesser extent the sun)
186) Why do moons orbit planets ?
Moons are moving quickly in a straight line, trying to fly away from the planet.
Meanwhile the planet's gravity is pulling the moon towards it. The two forces combine and the moon circles the planet.
© 2025 Better Solutions Limited. All Rights Reserved. © 2025 Better Solutions Limited TopPrevNext