Continuously Compounded (Future Value)
A very important aspect of compound interest calculations is the re-investment rate that is assumed.
Continuously compounded interest rates are used extensively when pricing derivatives.
In most cases and with all the Excel functions, the re-investment rate is assumed to be the same interest rate for each period.
This re-investment rate is assumed equivalent to the interest rate (or YTM) ??
Most equations in finance theory assume that interest is paid continuously compounded.
Continuously Compounded Interest
If the 10% interest rate is quoted with continuous compounding it means £100 invested for a year would increase to £??.
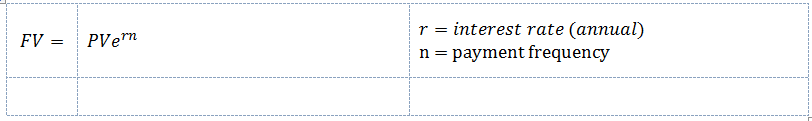 |
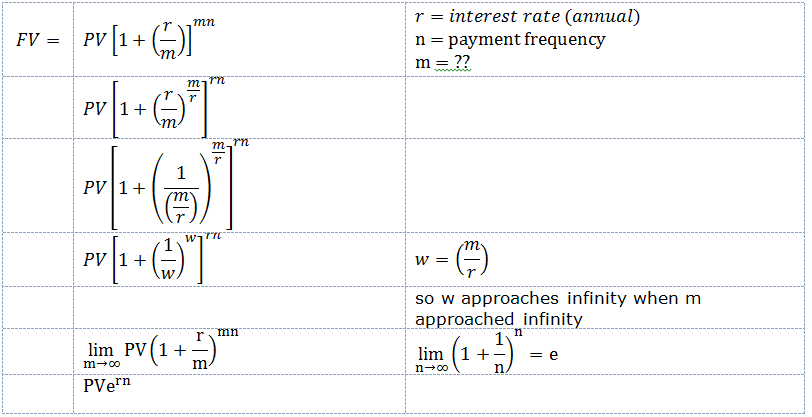
Continuously Compounded Interest Proof (limit)
The entire progression shows that a limit can be defined for continuous compounding (i.e. where m = infinity)
This is repeated at each interest payment date.
Interest paid "t" times a year at a rate of "r/t"
Now lets assume that these interest payments come at an increasingly frequent intervals but an increasingly smaller interest rate.
Lets take the limit t ---> infinity
This will lead to a rate of interest that is paid continuously.
 |
Continuously Compounded Interest Proof (differential equations)
Another way of deriving this equation is via an ordinary differential equation
Compounding a sum of money at a continuously compounded interest rate R for n years involves multiplying it by earn
Discounting a sum of money at a continuously compounded interest rate R for n years involves multiplying it by e-Rn
The compounding frequency defines the units in which an interest rate is measured.
Important
Continuously compounded interest is used in Quantitative finance.
The future value is also known as the compounded value.
© 2025 Better Solutions Limited. All Rights Reserved. © 2025 Better Solutions Limited TopPrevNext