VBA - Formulas Tab
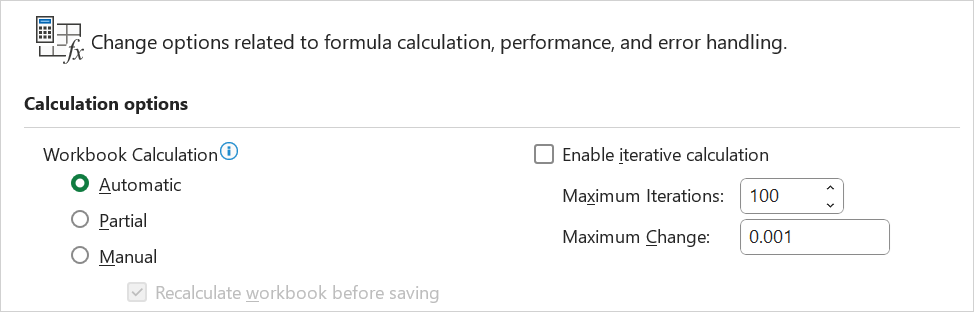
Calculation options
 |
Application.Calculation = xlCalculation.xlCalculationManual
Application.Calculation = Excel.xlManual
The second line is only made available for backwards compatibility.
Application.Calculation = xlCalculation.xlCalculationAutomatic
Application.Calculation = Excel.xlAutomatic
The second line is only made available for backwards compatibility.
Application.Calculation = xlCalculation.xlCalculationSemiautomatic
Application.Calculation = Excel.xlSemiautomatic
The second line is only made available for backwards compatibility.
Application.CalculateBeforeSave = True
Application.Calculate
ActiveSheet.Calculate
If you want to calculate just a selection of cells you could use Range("A2:E10").Calculate.
For more details on VBA Calculation, please refer to the Formulas > VBA Code > Calculation
Application.Iteration = True
Application.MaxIterations = 1000
Application.MaxChange = 0.001
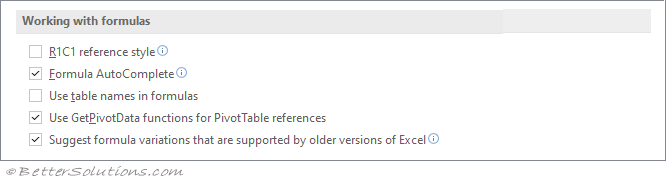
Working with formulas
 |
Error checking
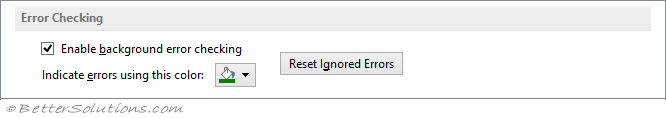 |
Enable background error checking
Creates a "divide by zero" error and displays the Error Checking Options smart tag.
Sub CheckBackground()
Application.ErrorCheckingOptions.BackgroundChecking = True
Range("A1").Select
ActiveCell.Formula = "=A2/A3"
End Sub
Indicate errors with this color
Returns or sets the color of the indicator for error checking options. Read/write XlColorIndex.
You can specify a particular color for the indicator by entering the corresponding index value. You can use the Colors property to return the current color palette.
Checks to see if the indicator color for error checking is set to the default system color and notifies the user accordingly.
Sub CheckIndexColor()
If Application.ErrorCheckingOptions.IndicatorColorIndex = xlColorIndexAutomatic Then
MsgBox "Your indicator color for error checking is set to the default system color."
Else
MsgBox "Your indicator color for error checking is not set to the default system color."
End If
End Sub
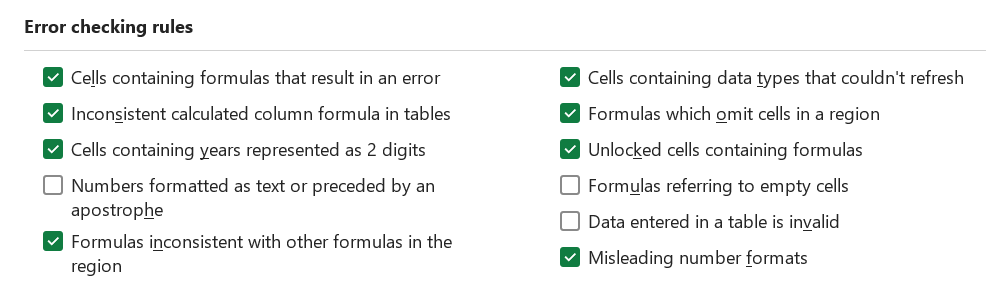
Error checking rules
 |
Application.ErrorCheckingOptions.EvaluateToError = True
Application.ErrorCheckingOptions.InconsistentTableFormula = True
Application.ErrorCheckingOptions.TextDate = True
Application.ErrorCheckingOptions.NumberAsText = True
Application.ErrorCheckingOptions.InconsistentFormula = True
Application.ErrorCheckingOptions.OmittedCells = True
Application.ErrorCheckingOptions.UnlockedFormulaCells = True
Application.ErrorCheckingOptions.EmptyCellReferences = True
Application.ErrorCheckingOptions.ListDataValidation = True
Application.ErrorCheckingOptions.MisleadingNumberFormats = True
Cells containing data types that couldn't refresh - no VBA
Cells containing stale values - no VBA
EvaluateToError
Creates a "divide by zero" error and displays the Error Checking Options smart tag.
Sub CellsContainingFormulasThatResultInAnError()
Application.ErrorCheckingOptions.EvaluateToError = True
Range("A1").Value = 1
Range("A2").Value = 0
Range("A3").Formula = "=A1/A2"
End Sub
InconsistentTableFormula
Creates a "divide by zero" error and displays the Error Checking Options smart tag.
Sub InconsistentCalculatedColumnFormulaInTables()
Application.ErrorCheckingOptions.InconsistentTableFormula = True
End Sub
TextDate
Enters a reference to a text date with a two-digit year and displays the Error Checking Options smart tag.
This example does not actually work.
Sub CellsContainingYearsRepresentedAs2Digits()
Application.ErrorCheckingOptions.TextDate = True
Range("B2").Value = "'April 23, 00"
End Sub
Perform check to see if 2 digit year TextDate check is on.
Sub CellsContainingYearsRepresentedAs2Digits_2()
Dim rngFormula As Range
Set rngFormula = Application.Range("A1")
Range("A1").Formula = "'April 23, 00"
Application.ErrorCheckingOptions.TextDate = True
If rngFormula.Errors.Item(xlTextDate).Value = True Then
MsgBox "The text date error checking feature is enabled."
Else
MsgBox "The text date error checking feature is not on."
End If
End Sub
NumberAsText
Enters a reference to a number stored as text and displays the Error Checking Options smart tag.
Sub NumbersFormattedAsTextOrPrecededByAnApostrophe()
Application.ErrorCheckingOptions.NumberAsText = True
Range("A1").Value = "'1"
End Sub
InconsistentFormula
Enters an inconsistent formula and displays the Error Checking Options smart tag.
Sub FormulasInconsistentWithOtherFormulasInTheRegion()
Application.ErrorCheckingOptions.InconsistentFormula = True
Range("A1:A3").Value = 1
Range("B1:B3").Value = 2
Range("C1:C3").Value = 3
Range("A4").Formula = "=SUM(A1:A3)" ' Consistent formula.
Range("B4").Formula = "=SUM(B1:B2)" ' Inconsistent formula.
Range("C4").Formula = "=SUM(C1:C3)" ' Consistent formula.
End Sub
Consistent formulas in the region must reside to the left and right or above and below the cell containing the inconsistent formula for the InconsistentFormula property to work properly.
OmittedCells
Enters a formula that refers to a range that omits adjacent cells that could be included and displays the Error Checking Options smart tag.
Sub FormulasWhichOmitCellsInARegion()
Application.ErrorCheckingOptions.OmittedCells = True
Range("A1").Value = 1
Range("A2").Value = 2
Range("A3").Value = 3
Range("A4").Formula = "=Sum(A1:A2)"
End Sub
UnLockedFormulaCells
Enters a formula in a cell that has been unlocked and displays the Error Checking Options smart tag.
Sub UnlockedCellsContainingFormulas()
Application.ErrorCheckingOptions.UnlockedFormulaCells = True
Range("A1").Value = 1
Range("A2").Value = 2
Range("A3").Formula = "=A1+A2"
Range("A3").Locked = False
End Sub
EmptyCellReferences
Enters a formula that refers to empty cells and displays the Error Checking Options smart tag.
Sub FormulasReferringToEmptyCells()
Application.ErrorCheckingOptions.EmptyCellReferences = True
Range("A1").Formula = "=A2+A3"
End Sub
ListDataValidation
Enter a value that is not in the data validation list and displays the Error Checking Options smart tag.
Sub DataEnteredInATableIsInvalid()
Application.ErrorCheckingOptions.ListDataValidation = True
End Sub
MisleadingNumberFormats
Enter a value that is not in the data validation list and displays the Error Checking Options smart tag.
Sub MisleadingNumberFormats()
Application.ErrorCheckingOptions.MisleadingNumberFormats = True
End Sub
© 2026 Better Solutions Limited. All Rights Reserved. © 2026 Better Solutions Limited TopPrevNext