VBA - Working with Arrays
Range to Array
The quickest way to populate an array with values in a cell range is to use a simple Variant data type.
You do not need to define the size of the array before it is populated.
This is only possible when the variable is defined as a Variant.
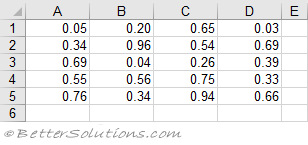 |
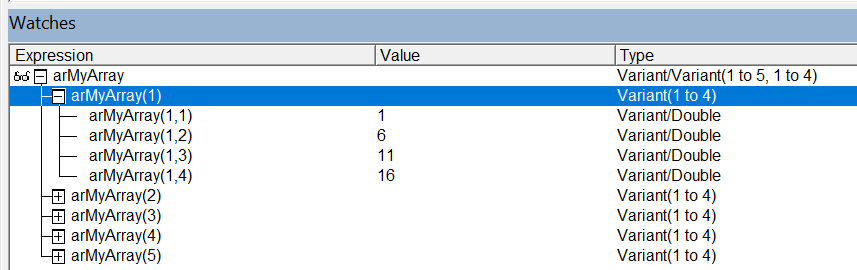
The array will always be 2 dimensional, it starts at 1 (not 0) and is always rows then columns.
Rows and Columns:
Dim arMyArray As Variant
arMyArray = Range("A1:D5").Value
 |
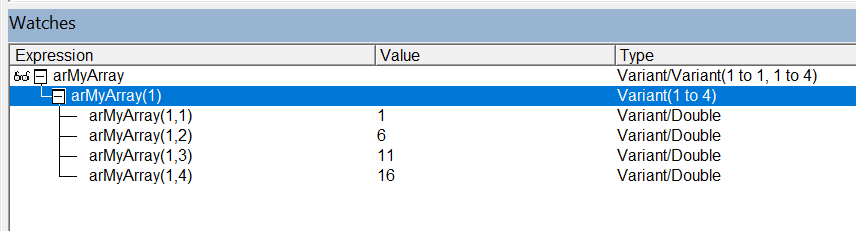
One Row:
Dim arMyArray As Variant
arMyArray = Range("A1:D1").Value
 |
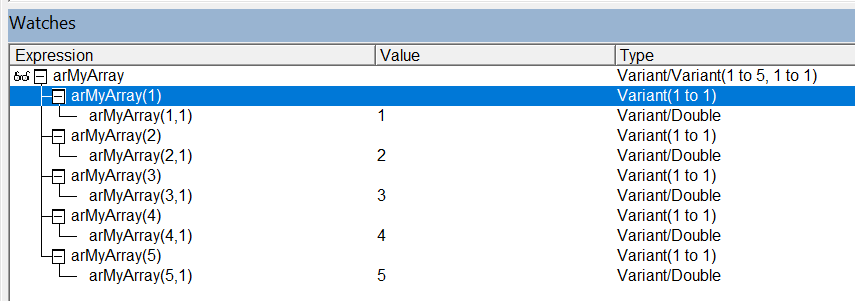
One Column:
Dim arMyArray As Variant
arMyArray = Range("A1:A5").Value
 |
Array to Range
The quickest way to populate a range with the contents of an array is to define the Value equal to the array.
Rows and Columns:
If you have a 2 dimensional array that you want to display on a worksheet you can assign the array to a Range.Value.
If the array has been populated with (rows, columns) the array can be assigned as it is.
Dim arValues As Variant
ReDim arValues(1 To 2, 1 To 3)
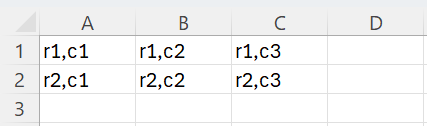
arValues(1, 1) = "r1,c1"
arValues(1, 2) = "r1,c2"
arValues(1, 3) = "r1,c3"
arValues(2, 1) = "r2,c1"
arValues(2, 2) = "r2,c2"
arValues(2, 3) = "r2,c3"
Range("A1:C2").Value = arValues
This will create the following table.
 |
If the array has been populated with (columns, rows) the array needs to be transposed first.
Dim arValues As Variant
ReDim arValues(1 To 3, 1 To 2)
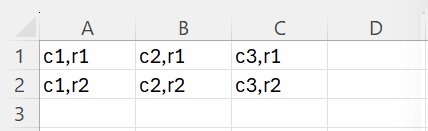
arValues(1, 1) = "c1,r1"
arValues(1, 2) = "c1,r2"
arValues(2, 1) = "c2,r1"
arValues(2, 2) = "c2,r2"
arValues(3, 1) = "c3,r1"
arValues(3, 2) = "c3,r2"
arValues = Application.WorksheetFunction.Transpose(arValues)
Range("A1:C2").Value = arValues
This will create the following table.
 |
One Row:
Note that this will create a horizontal array that will populate a row across the worksheet.
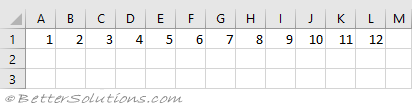
Dim arValues As Variant
arValues = VBA.Array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12)
Range("A1:L1").Value = arValues
This will create a table across the worksheet.
 |
One Column:
If you want to create a vertical array that will populate a column down the worksheet then you must transpose the array before assigning it to the Range.
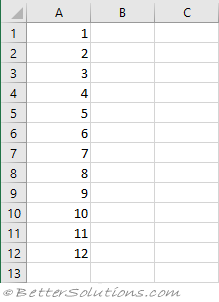
Dim arValues As Variant
arValues = VBA.Array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12)
arValues = Application.WorksheetFunction.Transpose(arTesting)
Range("A1:A12").Value = arValues
This will create a table down the worksheet.
 |
Empty Value
Dim aMyArray As Variant
aMyArray = Range("A1").Value
aMyArray has a value Empty if cell "A1" is empty
aMyArray = Range("A1").Value
aMyArray has the value if cell "A1" contains a value
Row and Column Vectors
Dim aMyArray As Variant
aMyArray = Range("A1:B1") 'row vector
aMyArray(1,1) = 1
aMyArray(1,2) = 2
Dim aMyArray As Variant
aMyArray = Range("A1:A2") 'column vector
aMyArray(1,1) = 1
aMyArray(2,1) = 2
Transposing the Array
Important
Excel reads FROM ranges a lot faster than it writes TO ranges.
© 2026 Better Solutions Limited. All Rights Reserved. © 2026 Better Solutions Limited TopPrevNext